Git squash commits with example
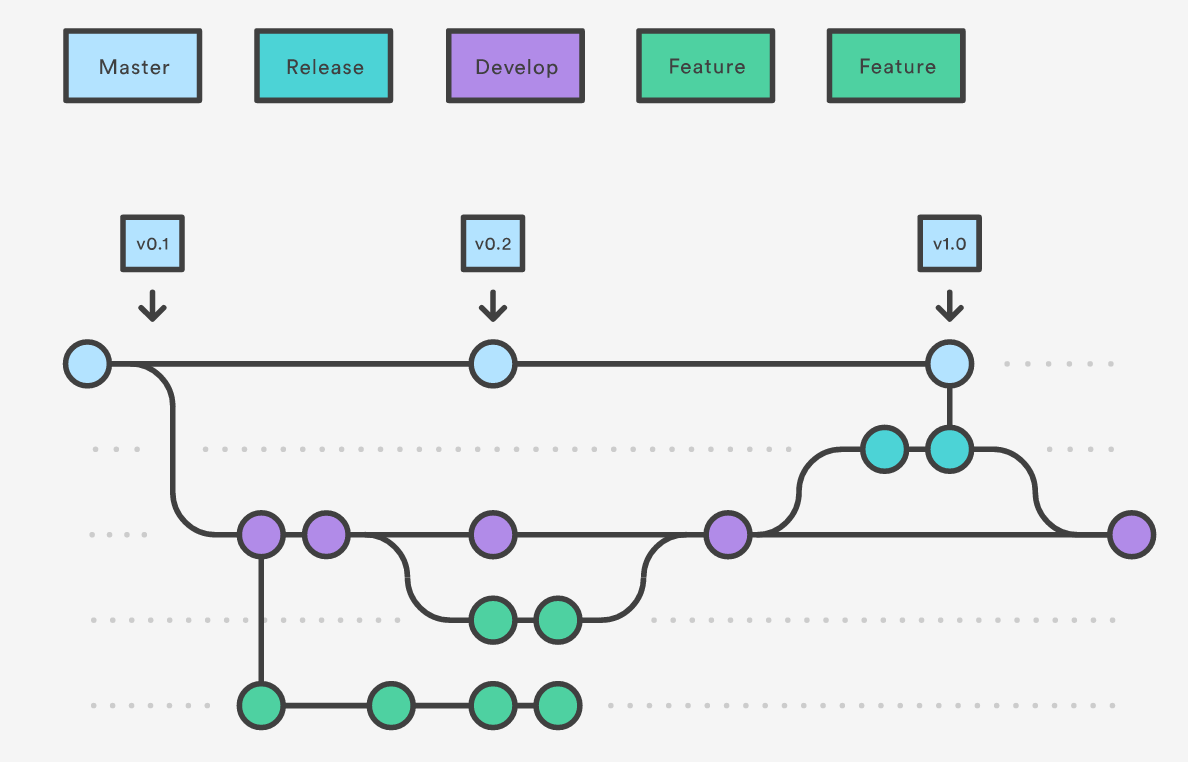
Summary
Squashing commits in Git allows you to combine multiple commits into a single commit. This can be useful when you have made multiple commits that should have been part of a single commit, or if you want to clean up your commit history.
Here’s an example of how to squash commits in Git repository:
- Start by checking out the branch that you want to squash commits on:
git checkout my-branch - Use the command
git logto view the list of commits on the branch. The most recent commit will be at the top. - Use the command
git rebase -i HEAD~n, where n is the number of commits from the top that you want to include in the squash. This will open a text editor with a list of the commits. - In the text editor, change the word “pick” at the beginning of each commit that you want to squash to “squash” or “s”
- Save and close the text editor.
- Git will prompt you to enter a new commit message for the squashed commit.
- After entering a new commit message, the squashed commit will be created and the branch will be updated with the new commit.
- Finally, use
git push -f <remote> <branch>to force push the branch to the remote repository to update the branch with the squashed commits.
Note: Be careful when squashing commits that have been pushed to a remote repository, as it will change the commit history and can cause issues for other collaborators.

 Never miss a
story from us, subscribe to our newsletter
Never miss a
story from us, subscribe to our newsletter